Skip to main content
What are you looking for?
Print
The Future Of Work: 8 steps through which automation is driving transformation.
Updated
ByMichael Osoho
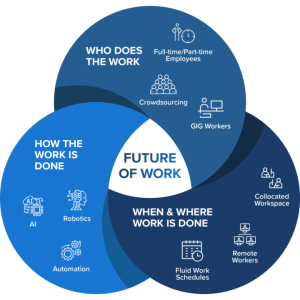
Automation is reshaping industries by streamlining processes, increasing efficiency, and reducing costs. In the future of work, we’ll see more widespread adoption of robotic process automation (RPA), artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML) technologies across various sectors. This will lead to the transformation of job roles, with an emphasis on tasks that require human creativity, critical thinking, and emotional intelligence.
Up skilling and re skilling programs will become crucial to ensure workers can adapt to the changing demands of their industries. Automation is reshaping industries across the globe, revolutionising processes, enhancing efficiency, and transforming business models.
Here are the general steps through which automation is driving this transformation:
1. Identification of Tasks: The first step in automation is identifying repetitive, rule-based tasks that can be performed by machines or software. These tasks are typically time-consuming for humans and are prone to errors. Industries analyze their workflows to pinpoint such tasks across various departments and functions.
2. Technology Selection: Once tasks are identified, organizations select appropriate automation technologies to streamline these processes. This could involve choosing robotic process automation (RPA) software, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), or other specialized tools depending on the nature of the tasks.
3. Integration and Implementation: Automation technologies are integrated into existing systems and workflows. This may require collaboration between IT teams, software developers, and process experts to ensure seamless integration and minimal disruption to operations.
4. Training and Up skilling: Employees who were previously responsible for performing manual tasks now need to be trained in operating and managing automated systems. Upskilling programs are often implemented to equip workers with the necessary knowledge and skills to adapt to the changing work environment.
5. Testing and Optimisation: Automated systems undergo rigorous testing to ensure they function as intended and deliver the desired results. Continuous monitoring and optimisation are essential to fine-tune automation processes, improve efficiency, and address any issues that arise.
6. Scale and Expansion: Once automation is successfully implemented and proven effective, organisations often scale up their efforts by automating additional tasks and processes. This may involve expanding automation to different departments, branches, or regions within the organization.
7. Data Analysis and Decision-Making: Automation generates vast amounts of data that can be analysed to gain insights into operational performance, customer behaviour, and market trends. This data-driven approach enables organisations to make informed decisions, optimise processes further, and identify new opportunities for innovation.
8 Continuous Learning and Evolution: Automation is not a one-time event but an ongoing journey of continuous learning and evolution. Industries must remain agile and adaptable, embracing new technologies and innovations to stay ahead of the curve and drive sustainable growth in the long term.
By following these steps, industries can harness the power of automation to unlock new opportunities, improve productivity, and drive innovation across their organizations.
Posted
Updated
ByMichael Osoho
Tags:
Table of Contents